Pes Cavus
1. Causes / Sequelae
a. Trauma
b. Neuromuscular Causes (NM)
- CNS: Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Spinal Cord: Spina Bifida
- Peripheral Nerve (PNS): Lower Motor Neuron lesions (e.g., CMT)
- Muscular: Muscular Dystrophy
Most Common Cause - Bilateral: Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease
- Unilateral: Spinal cord tumor
2. Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) Disease
- Inheritance: Autosomal Dominant (AD) — most common
- Defect: PMP22 gene on Chromosome 17
- Recessive forms: Rare, more aggressive
Pathophysiology
- Imbalance between flexors and extensors due to weakness
- TA (Tibialis Anterior) and Peroneus longus imbalance
- 1st ray plantar flexion → longus overactivity
- Heel varus due to tripod effect
Types
- Clawing: due to excessive extensor recruitment
- Equinus: due to gastrosoleus overpull
CMT Variants
| Type | Inheritance | Pathology | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | AD | Demyelination | Common |
| Type 2 | AD | Axonal loss | Moderate |
| Type 3 | AR | Degenerative (severe, in infants) | Rare |
3. Clinical Features
- Identify heel varus and cavus
- Dynamic clawing observed during walking
- Coleman Block Test — differentiates flexible vs. rigid deformity
- Power testing & reflexes — identify neurological involvement
- Silfverskiöld test — to assess gastrocnemius vs. soleus tightness
- Examine spine and hand — for associated deformities
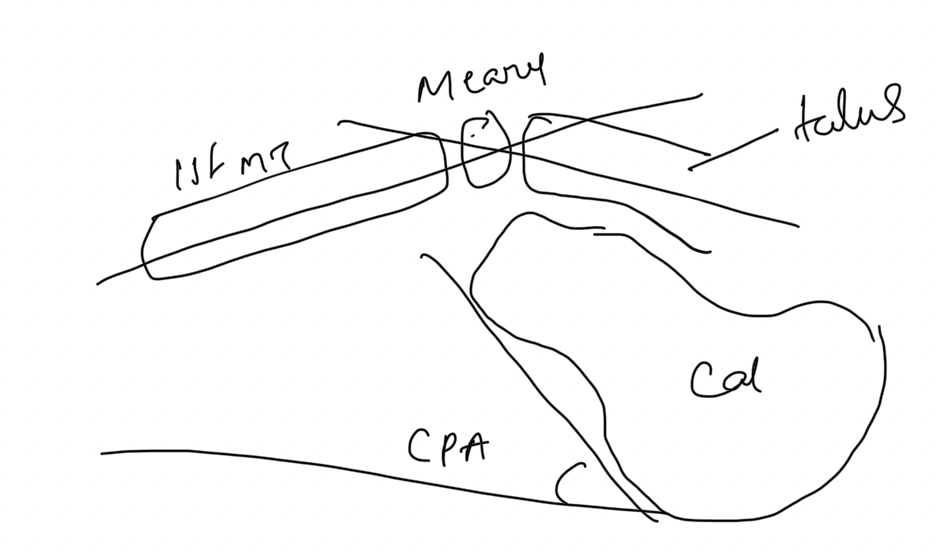
4. Radiological Features
Lateral X-ray Findings - Large, anterior apex Meary’s angle - Increased calcaneal pitch
5. Management
A. Non-Surgical
Footwear Modifications
| Deformity | Footwear Correction |
|---|---|
| Gastrosoleus tightness | Heel lift |
| Hindfoot varus | Medial heel cup + lateral posting |
| High arch | Arch support (reduce forefoot pressure) |
| Claw toes | Metatarsal bar (redistribute contact pressure) |
B. Surgical
Principles
Aim: Stable, plantigrade, painless, flexible foot
Achieved by: 1. Bringing heel under leg
2. Correcting deformities to fit shoe
3. Balancing muscle forces
6. Surgical Procedures
- 1st Ray:
- Plantar flexion correction → Dorsiflexion osteotomy
- Cavus:
- Plantar fascia release
- Varus:
- Lateral closing wedge calcaneal osteotomy
- Equinus:
- Tendo-Achilles lengthening
- Claw Toes:
- Flexible deformity: Flexor-to-extensor transfer (EDL, EHL)
- Fixed deformity:
- PIP joint fusion (Weil procedure)
- PIP joint excision
- MTP joint release
- PIP joint fusion (Weil procedure)
- Flexible deformity: Flexor-to-extensor transfer (EDL, EHL)
Big Toe (Hallux):
- MTP fusion + EHL to EPL transfer
Summary Table
| Deformity | Correction |
|---|---|
| 1st Ray | Dorsiflexion osteotomy |
| Cavus | Plantar fascia release |
| Varus | Lateral wedge calcaneal osteotomy |
| Equinus | Tendo-Achilles lengthening |
| Claw Toes | Flexor to extensor transfer / PIP fusion |